Graphics Processing Unit (GPU)
In my last blog, I quickly introduced to DeepSeek and some of the components the used. In this blog, we will get down to basics of GPU and specifically NVIDIA GPU architecture, how CUDA programs gets compiled.
CPU vs GPU
What is the difference between a CPU and GPU?
A> CPUs are for general-purpose computing where as GPUs are optimized for performing same operations on multuple data points simultaneously achieveing in high level of parallelism.
B> CPUs are best suited which runnign complex logic where as GPUs are ideally for massively parallel computations like graphics rendering, deep learning and scientific simulations.
C> CPU is optimized for low-latency access to relatively small amount of memory. GPU is typically used for high-bandwidth to large amount of dataset in parallel.
GPU
Here's a quick introduction to GPU, it's architecture and CUDA programming workflow.
The cuda program workflow is as shown below. It starts off with your program which has extension of ".cu". This code can be written in C, C++ or Fortran.
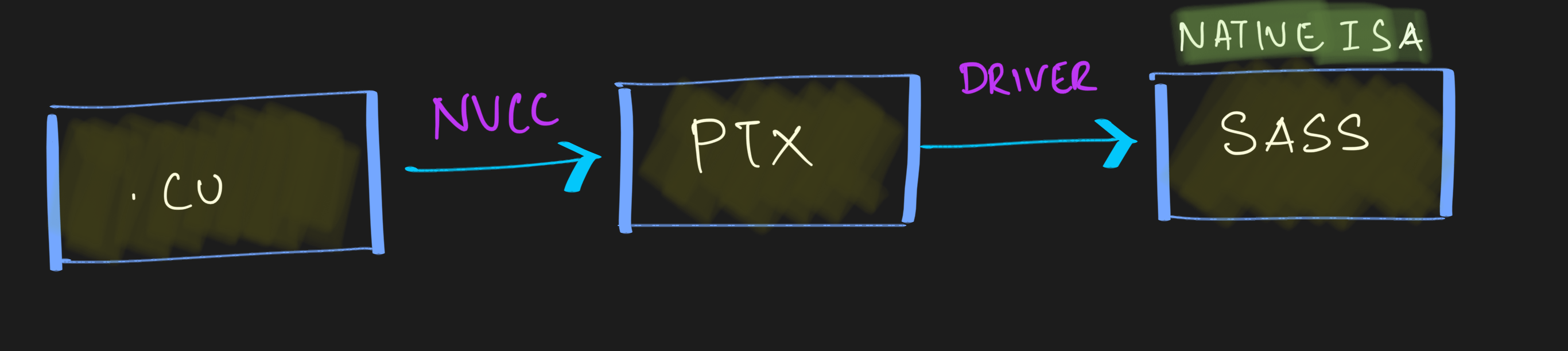
Basic Flow
This is a very basic flow of a CUDA program.
Detailed Workflow
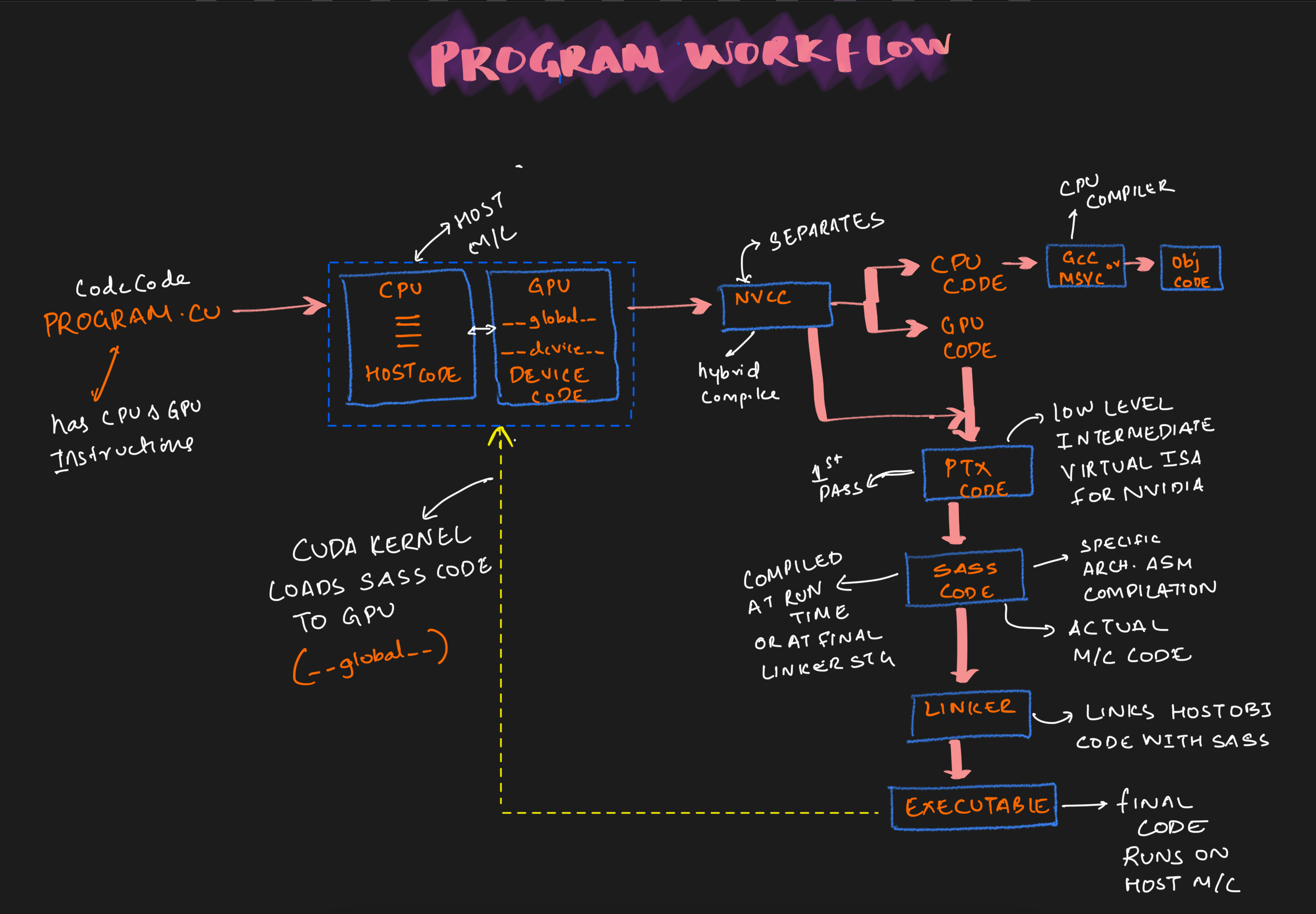
Typically these programs has both CPU and GPU instructions running on host machine. The CPU piece of code is called the host code and GPU code section is called device code typically which has global and device function.
This code is compiled using NVCC compiler separating both the CPU and GPU code. The CPU code uses CPU complier like GCC converting to the object code.
At the same time the 1st pass of the GPU converts the GPU code is converted to PTX code. This is a low level IR (Intermediate Representation) is then compiled to convert it to device specific code known as SASS code.
Final stage is to link the host object code with SASS and run the code to run on host machine.
PTX is an abstraction layer helping code portabiloty between NVIDIA decides. This helps tools and libraries to manupulate code code before GPU execution, an approach whichDeepSeek team did. We will have a separate article going over the PTX.
Structure
Before we delve deeper into the PTX optimization by DeepSeek, let us first talk about GPU .
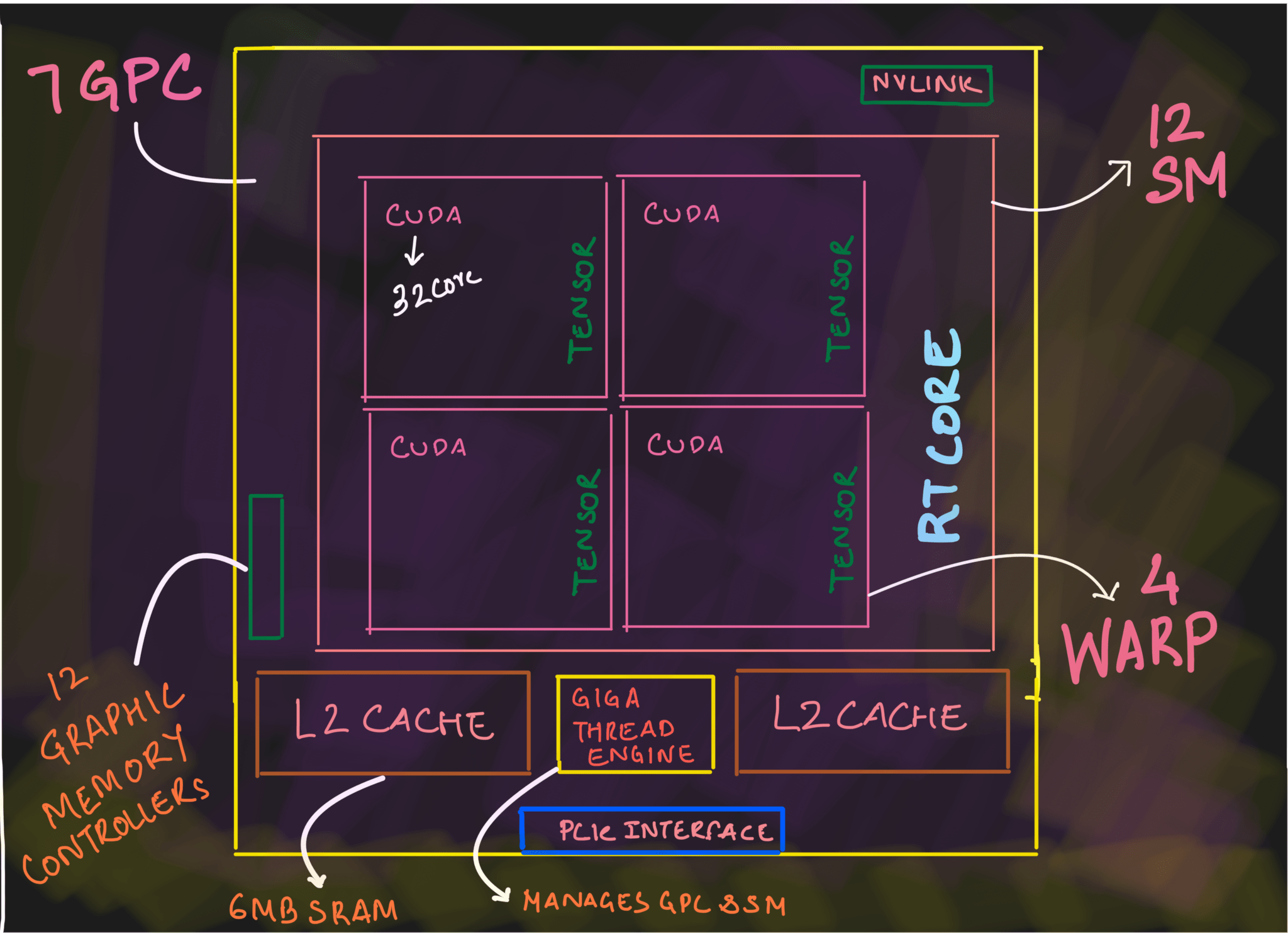
There are :
- 7 Graphic Processing Clusters (GPC)
- Each GPC had 12 Streaming Multiprocessors (SM).
- Every SM will have 4 Warps and 1 Ray Tracing core
- A single Warp will have 32 CUDA core and 1 Tensor Code.
- 12 Graphic Memory Controllers
- Two L2 Cache of 6MB SRAM each
- NVLink
- PCIe Interface
So in total in one NVDIA GPU there could be about :
10752CUDA cores
336Tensor cores
84Ray tracing cores
Core
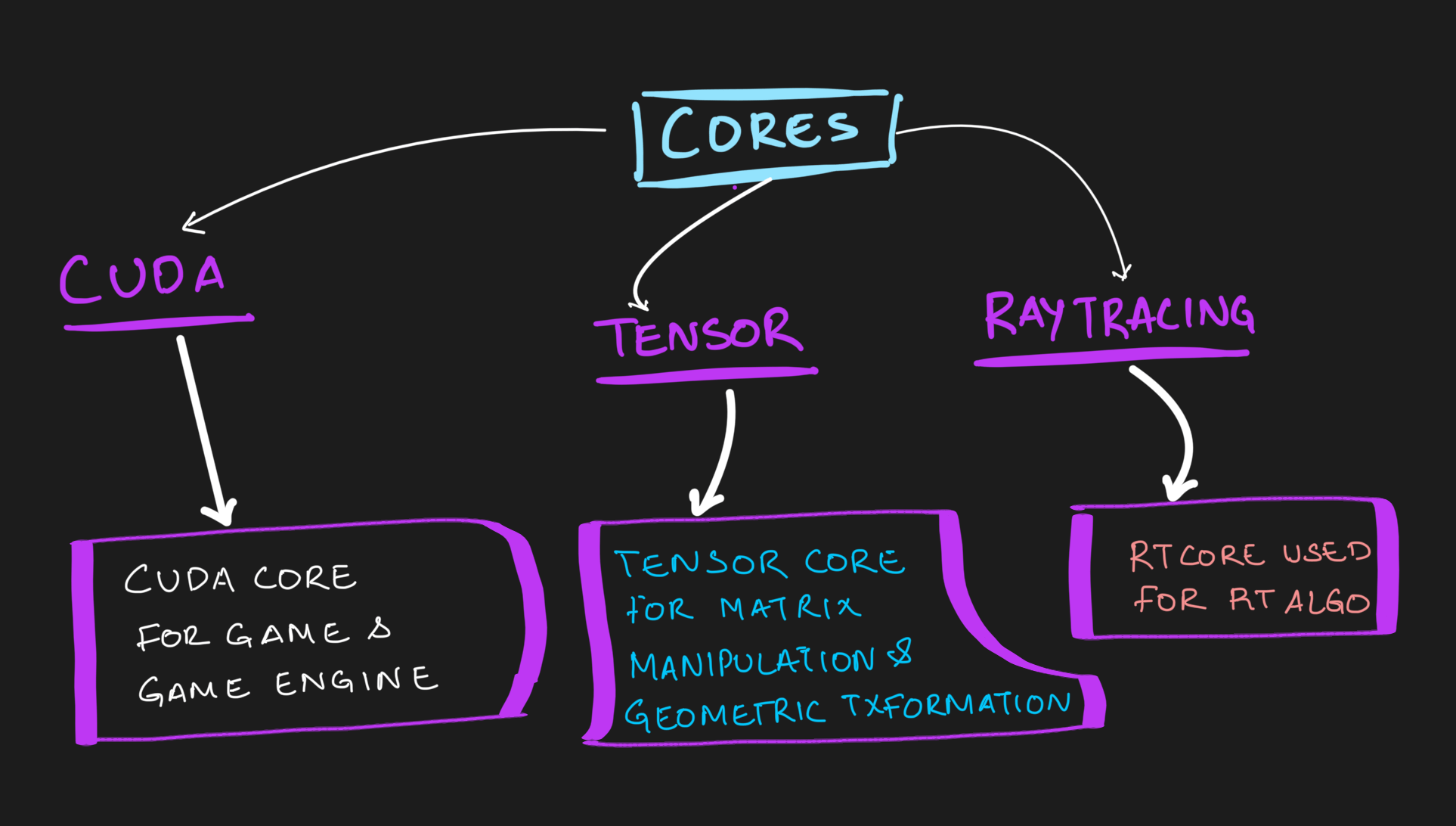
Here are the three cores available in these GPUs
- CUDA Core is used for game and game engines.
- Tensor Core is exclusively for Matrix Multiplication and Geometric Transformation which is used in AI/ML
- Ray Tracing is used ror Ray Tracing algorithms.
Next Steps
With basic introduction to GPU out of the way. let us move to PTX. See you in my next arcticle.