LLM Overview
Large Language Models
OpenAI has been at the forefront of developing sophisticated LLMs, often perceived as black boxes. Until DeepSeek's open-source release, that is. Now, we have a unique opportunity to peek behind the curtain. In this series of articles, I will delve into the inner workings of DeepSeek's LLMs, starting with the basics before moving on to more advanced topics, covering their architecture and optimization techniques. Here are some of my notes exploring their research papers.
Background
DeepSeek has emerged as a significant disruptor in the AI industry, particularly in the realm of large language models (LLMs). It gained recognition for achieving high-level AI performance while utilizing significantly fewer computational resources compared to industry giants like OpenAI.
DeepSeek leverages techniques like "Mixture of Experts (MoE)" to optimize resource allocation, innovations like Multi-Head Latent Attention (MLA) etc among many others. But the most important breakthrough was their commitment to open-source principles contributing to its rapid growth and influence.
Impact
DeepSeek's success has put pressure on established AI companies to reconsider their development strategies and by democratizing their AI technology, it has made these models more accessible to smaller organizations and developing nations.
They developed a model much more powerful (or similar) than OpenAI with significantly less resource. DeepSeek's rise signifies a shift towards more efficient and accessible AI, challenging the dominance of OpenAI.
My Motivation
DeepSeek's achievement, building a powerful model with optimized resources, resonates deeply. It's a testament to human ingenuity, a reminder that constraints often spark the most innovative solutions. When faced with limitations, we have an incredible ability to find efficient, impactful pathways forward.
We've always defined ourselves by the ability to overcome the impossible. And we count these moments. These moments when we dare to aim higher, to break barriers, to reach for the stars, to make the unknown known. We count these moments as our proudest achievements. But we lost all that. Or perhaps we've just forgotten that we are still pioneers. And we've barely begun. And that our greatest accomplishments cannot be behind us, because our destiny lies above us. - Cooper, (Movie - Interstellar)
LLM Architecture
Let us see a simple structure of LLM Architecture containing three blocks
- Input
- Transformer
- Output
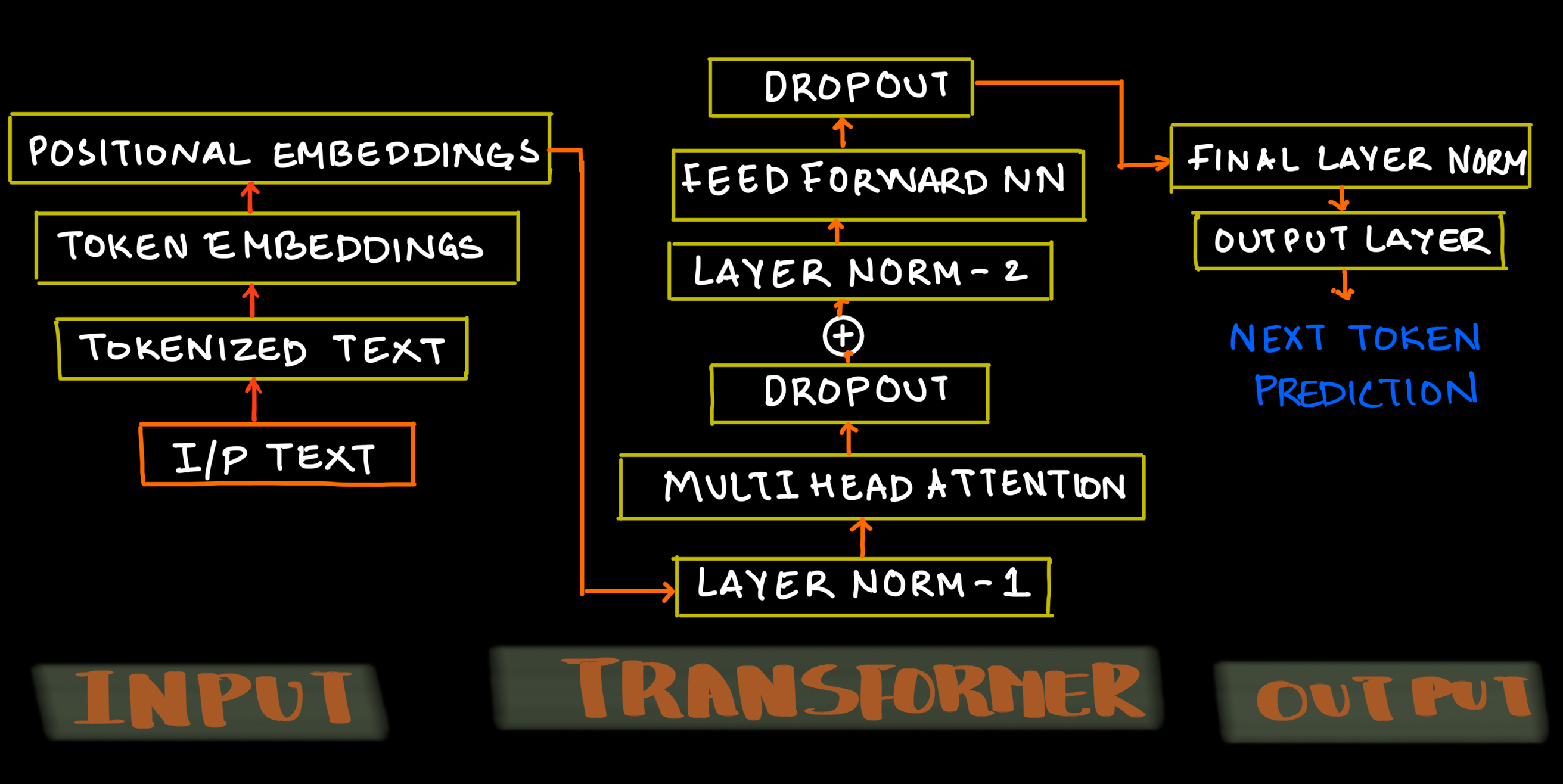
Input Block
Input block will process text by tokenizing it and using Embedding layer will create a token embedding. This token embedding layer will be added to positional encoding creating final Input embedding matrix
Output Block
This is where the next token will be predicted. Output of transformer block is normalized and send it to logist layer where the word with highest probability is choosen.
Transformer Block
All the magic happens here. DeepSeek replaced Multi-Head Attention with Multi-Head Latent Attention along with other innovations in the LLM architecture.
DeepSeek's Archictecure
Multi-Head Latent Attention
Mixture of Experts (MoE)
Multi-Token Prediction
Reinforcement Learning using GRPO
GPU Optimization via PTX
Conclusion
This blog series (converted from my research notes) will provide a glimpse into the architecture and optimization of foundational LLMs, culminating in a deeper understanding of DeepSeek's architecture, equipping you with a solid foundation to embark on your own LLM research. The open sourcing of LLMs, and DeepSeek in particular, is a major step in the democratization of AI. The rapid evolution of these models promises to reshape how we interact with technology.
Enjoy your reading!